The Times of India Article Rating
The Times of India Article RatingHeat-related deaths up 23% globally since 1990s: Lancet | India News - The Times of India
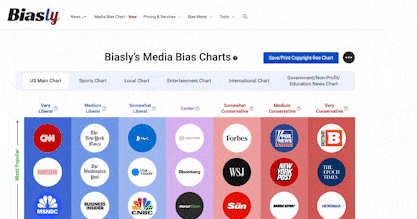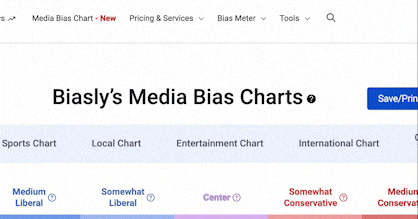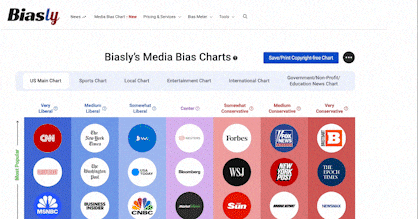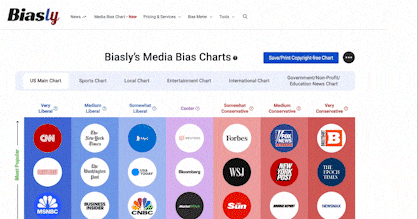
- Bias Rating
- Reliability
40% ReliableAverage
- Policy Leaning
-10% Center
- Politician Portrayal
N/A
Continue For Free
Create your free account to see the in-depth bias analytics and more.
By creating an account, you agree to our Terms and Privacy Policy, and subscribe to email updates.
Bias Score Analysis
The A.I. bias rating includes policy and politician portrayal leanings based on the author’s tone found in the article using machine learning. Bias scores are on a scale of -100% to 100% with higher negative scores being more liberal and higher positive scores being more conservative, and 0% being neutral.
Sentiments
-18% Negative
- Liberal
- Conservative
| Sentence | Sentiment | Bias |
|---|---|---|
Unlock this feature by upgrading to the Pro plan. | ||
Reliability Score Analysis
Policy Leaning Analysis
Politician Portrayal Analysis
Bias Meter
Extremely
Liberal
Very
Liberal
Moderately
Liberal
Somewhat Liberal
Center
Somewhat Conservative
Moderately
Conservative
Very
Conservative
Extremely
Conservative
-100%
Liberal
100%
Conservative
Contributing sentiments towards policy:
52% : Health is impacted by a number of factors which include food habits, occupational habits, socio-economic status, medical history, immunity, heredity, etc., of individuals apart from the environment," environment ministry has told Parliament a number of times on the question of linking deaths exclusively with air pollution.Authored by 128 experts, the report noted the continued dependence on fossil fuels also puts an unbearable strain on countries' budgets, with govts collectively spending $956 billion on net fossil fuel subsidies in 2023.48% : He writes on environment, climate change, agriculture, water resources and clean energy, tracking policy issues and climate diplomacy.
43% : India, the report, released Wednesday, said there were over 17,18,000 deaths attributable to anthropogenic air pollution (PM2.5) in 2022, an increase of 38% since 2010, whereas fossil fuels (coal and liquid gas) contributed to 7,52,000 (44%) of the deaths while coal alone accounted for 3,94,000 deaths, primarily from its use in power plants (2,98,000 deaths).
39% : Underlining how the continued over-reliance on fossil fuels and failure to adapt to climate change is being paid for in people's lives, health and livelihoods, the report said the air pollution resulting from the continued burning of fossil fuels has resulted in a staggering 2.5 million deaths globally every year.It also said the global average transmission potential of dengue has risen by up to 49% since the 1950s, and linked even such a rise in India during 2015-24, compared to 1951-1960, to climate change.On
*Our bias meter rating uses data science including sentiment analysis, machine learning and our proprietary algorithm for determining biases in news articles. Bias scores are on a scale of -100% to 100% with higher negative scores being more liberal and higher positive scores being more conservative, and 0% being neutral. The rating is an independent analysis and is not affiliated nor sponsored by the news source or any other organization.