Yahoo News Article Rating
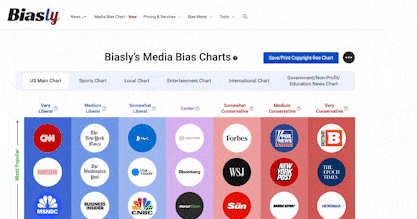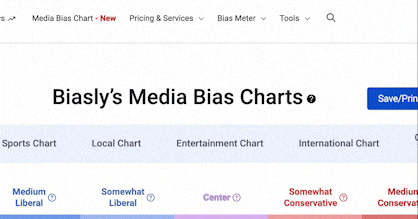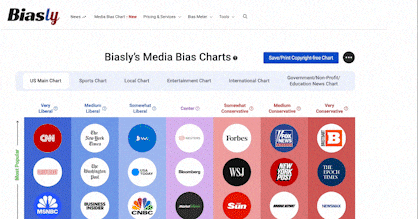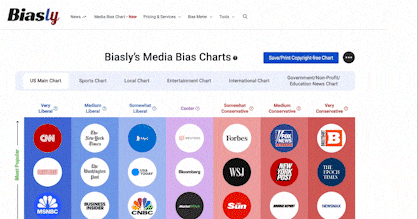
Yahoo News Article RatingIn Cities With School Choice, Low-Income Kids Catching up to Wealthier Peers
- Bias Rating
- Reliability
85% ReliableGood
- Policy Leaning
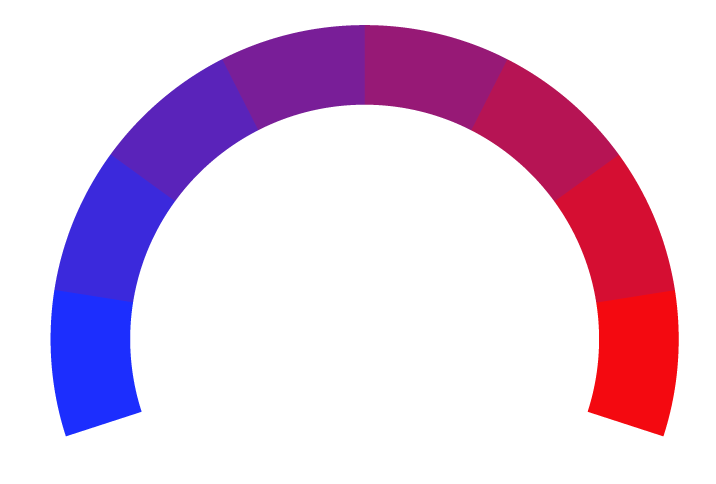
16% Somewhat Right
- Politician Portrayal
N/A
Continue For Free
Create your free account to see the in-depth bias analytics and more.
By creating an account, you agree to our Terms and Privacy Policy, and subscribe to email updates.
Bias Score Analysis
The A.I. bias rating includes policy and politician portrayal leanings based on the author’s tone found in the article using machine learning. Bias scores are on a scale of -100% to 100% with higher negative scores being more liberal and higher positive scores being more conservative, and 0% being neutral.
Sentiments
4% Positive
- Conservative
| Sentence | Sentiment | Bias |
|---|---|---|
Unlock this feature by upgrading to the Pro plan. | ||
Reliability Score Analysis
Policy Leaning Analysis
Politician Portrayal Analysis
Bias Meter
Extremely
Liberal
Very
Liberal
Moderately
Liberal
Somewhat Liberal
Center
Somewhat Conservative
Moderately
Conservative
Very
Conservative
Extremely
Conservative
-100%
Liberal
100%
Conservative
Contributing sentiments towards policy:
53% : And in St. Louis, where 39% of students are enrolled in public charter schools, the performance gap closed by 30%.52% : In Kansas City, where 46% of students are enrolled in public charter schools, the performance gap between low-income students and all students closed by 31% between the 2010-11 school year and 2022-23.
52% : The report found that in the city, where 58% of students are enrolled in public charter schools or innovation schools, the performance gap between low-income students and all kids statewide closed by 23% between the 2010-11 and 2022-23 school years.
51% : " New Jersey is home to another standout in PPI's report: Newark, where 35% of students are enrolled in public charter schools and the performance gap closed by 45% across the same 12-year period.
*Our bias meter rating uses data science including sentiment analysis, machine learning and our proprietary algorithm for determining biases in news articles. Bias scores are on a scale of -100% to 100% with higher negative scores being more liberal and higher positive scores being more conservative, and 0% being neutral. The rating is an independent analysis and is not affiliated nor sponsored by the news source or any other organization.