News sources are not just a modern vehicle for information, but have had a continuously growing presence within the world as the trajectory of globalization has climbed. News sources are not restricted to traditional outlets such as formally published newspapers, but also encompass online news sites, blogs, social media platforms, and people spreading information from word of mouth. This translates into an increase in the accessibility of real-time information in many regions across the globe, so people can learn about major events and gain an in-depth view of the people and countries affected.
News sources can be the catalyst for action, reaction, or lack thereof. For example, during Hurricane Katrina, the reports from both journalists and victims elicited an outpouring of support and much-needed aid from around the world. News sources reach a wide audience and more specifically each individual that comprises their audience which means that they deeply affect our emotions and opinions. Therefore, it is incredibly important that we understand where news is coming from in order to accurately determine the reliability of the source.
What Is News Source Reliability and How To Check News Source Reliability?
News source reliability determines how trustworthy a news source’s information is based on its accuracy, fairness in providing a multitude of perspectives, and reporting facts devoid of personal bias. However, it must also be acknowledged that bias is implicit and is neither inherently negative nor positive, but it does inform people’s opinions and beliefs. This consequently emphasizes the importance of obtaining reliable information. “Reliable information must come from dependable sources…a reliable source will provide a ‘thorough, well-reasoned theory, argument, etc. based on strong evidence.” According to Stevenson University, examples of dependable sources come in the form of peer-reviewed articles, news articles from heavily reviewed/critiqued, established companies, or peer-reviewed and professionally published books.
And a few primary questions to use as a frame of reference when examining a source are: Who is the author? How accurate is this information based on what I already know? Is this information relevant?
Paying special care to titles and headlines is also a way to eliminate more problematic sources through a cursory glance. Emboldened headlines with flashy words either antagonistic or overly sympathetic are indicative of a specific way a source is framing its information for audience retention in addition to enticing viewers to their desired perspective or position. With such a large population, it is paramount in educating and reporting to the public about issues regardless of their weight on current events, but it must also be acknowledged that sensationalizing this information detracts from the importance and urgency that these matters should be handled with.
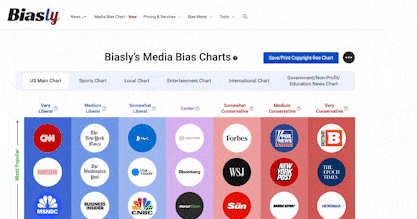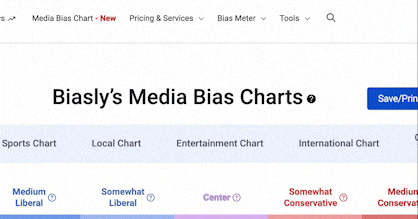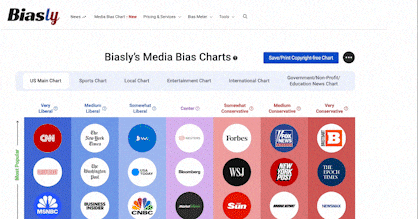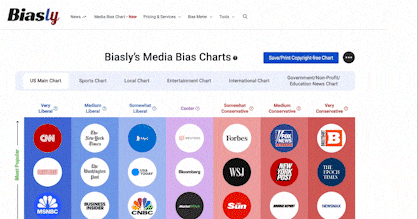
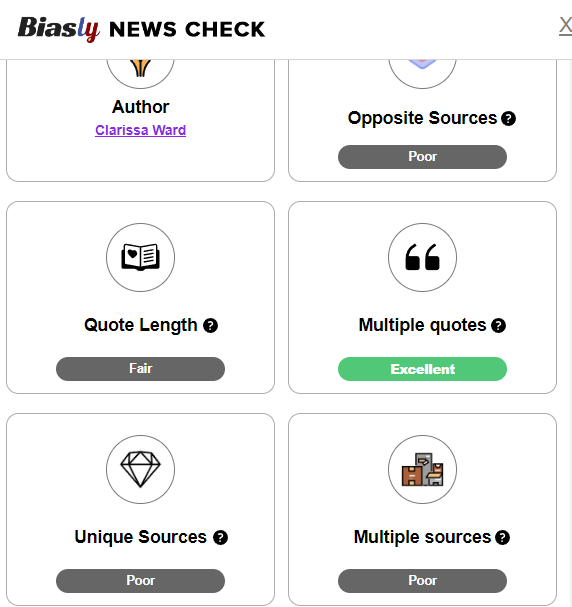
However, there is an overwhelming number of media outlets in addition to the new and pre-existing social media platforms that have contributed to the outpouring of information making it difficult to comprehend or keep up with. Biasly is a company that uses its “Bias Meter” to give its users information about bias within the news content they are viewing, streamlining the research aspect of checking news source reliability making it a useful tool for every audience.
Why Is News Source Reliability Important?
News source reliability is important because it allows people to analyze evidence and facts better in order to make the best possible decision, whether it be voting or supporting a cause for oneself and others. Depending on a source, thoughts and opinions may have been induced by the context or rhetoric used to deliver the news causing people to come to conclusions that they have been led to believe rather than exploring their beliefs or values and basing opinions on those. The skill of discovering a reliable source has also become more and more pertinent with the integration of social media into society. Through the internet and social media, misinformation and disinformation can easily gain traction through likes and shares becoming more pervasive and harmful. “The terms “misinformation” and “disinformation” are often time used interchangeably…The difference between the two lies in the intent: where “misinformation” is loosely defined as untrue, or semi-truthful content presented as fact, “disinformation” is defined as untrue, or semi-truthful content, deliberately.” Due to the growing influence of “fake news” and “alternative facts,” it is imperative that checking the credibility and reliability of sources becomes habitual for the younger generation as well as the older generations.
Mainstream Media vs Alternative Media
As mainstream news clashes over bias and political leaning, many have sought to find their news elsewhere through alternative sources. We often refer to these sources as “alternative media.” Alternative media can take many forms, but it is most often found on social media websites like Twitter and Youtube. Many of these sources are innocent or focus on events that mainstream media do not cover, like Chinese investment in Africa or daily reports from the war in Ukraine. Unfortunately, alternative media also offers an outlet for unsubstantiated stories and conspiracy theories.
Let’s start with definitions. Mainstream media often has its own domains, websites, or TV channels. CNN, MSNBC, Fox News, The Economist, and Reuters are all examples of mainstream media. Alternative media typically uses social media to disseminate information and promote their own brand. The information and quality of content can vary drastically and is often under less scrutiny than mainstream outlets. They can range from conspiracy platforms like Infowars, to far-right publications like Breitbart or News Max, to independent left-leaning media like the David Pakman show or far-left radio shows like The Majority Report. It is important to reiterate that alternative media can vary drastically in the accuracy of their reporting and the topics they cover. Oftentimes they cover mainstream media reporting in the context of their own political opinions.
This being said, bias is not inherently a good or bad thing. Reliable information exists independent of the author’s bias. What bias can do is influence the author’s analysis of a news story, and what pieces of evidence make their way into a report. Many aspects of our society rely on receiving correct information. From business to elections, perfect information is the assumption on which we analyze decisions. If we were to receive different information, we will make different decisions. We obviously want to make the best decisions possible, so we need reliable information.
Let’s look at a few examples to get a good grasp of reliable and unreliable information.
Reliable News Examples
Let’s first start with reliability examples. Reliable news can take many forms, but it usually embraces several of the following characteristics:
- Multiple verified sources
- Competitive publication
- Direct quotations
- Minimal author analysis, and
- Transparency
If multiple news organizations publish a similar story, it’s most likely true.
Most news organizations are competing with each other for viewers and subscribers, and this competition holds them to relatively high standards. Alternative media generally finds a niche community to cater its product to, so it is generally non-competitive. Mainstream media also has the responsibility of providing more accountability, and if a news station makes a major mistake there are legal and shareholder consequences. Direct quotations and documents are as close as possible to a primary source, so new stories that focus on these contain more truth.
Author analysis is generally where bias manifests itself. If an author writes their thoughts, it doesn’t invalidate the entirety of the article, but it should be taken into account. Lastly, transparency in news organizations helps build trust in their sources and their writing. Obviously, on issues of national security, news organizations don’t want to compromise their sources. In general, however, news organizations that do not cite their sources are often untrustworthy.
News Misinformation Examples
This article is from Reuters and is a nice example of misinformation in which it makes public its media accountability practices. Biasly rates Reuters as a center-leaning news source with outstanding accuracy. Many other news stations use Reuters reporting, as a standard, for their political news reporting. The article regarding Xi Jinping’s third term features different political researchers with quotations and analyses.
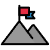
The key feature of misinformation is that it is not done with malicious intent. Oftentimes, you will find misinformation posted on social media in the form of pictures or graphs. People will misinterpret data or research without understanding the information being presented. The following is a popular example circulated during the COVID pandemic.
This image was widely circulated as proof Ivermectin was an effective treatment for COVID. By downloading the pdf file at the top of the image, we can see that the source for this graph is lackluster (Preprint is here). The methodology is a retrospective statistical analysis study. Retrospective means that the data doesn’t come from an experiment where factors were controlled for. Few to no medicinal research is done using retrospective studies. The “Note” at the bottom of the first page also mentions that this paper is a preprint, meaning that it isn’t peer-reviewed, and “should not be used to guide clinical practice.” Almost anyone can submit a preprint, so it should not be taken at face value.
For medical treatment, researchers will often use double-blind prospective studies. This means that subjects are specifically chosen to be similar, all factors outside of treatment are controlled, and neither the researchers nor subjects know if they are distributing/receiving a placebo. This means that only differences in symptoms and recovery can be measured by the head researchers. Most drug-related agencies across the world use this as a gold standard for medicinal drug approval. This study fulfills this and shows that Ivermectin does not make a meaningful difference as a COVID treatment.
Academic articles that are peer-reviewed are the best source of information possible as they have passed numerous processes of accountability. Many news stations will simplify this information, however, so be careful while reading second-hand reporting.
News Disinformation Examples
Disinformation is done with malicious intent. It is mostly seen in foreign propaganda or in terrorist campaigns. The purpose is to confuse the general audience or to sow doubt in otherwise reputable sources. The main difference between disinformation and misinformation is that disinformation is created in bad faith. This being said, disinformation can be reposted by people who do not know any better, so it is best to try and track down the source of inflammatory claims.
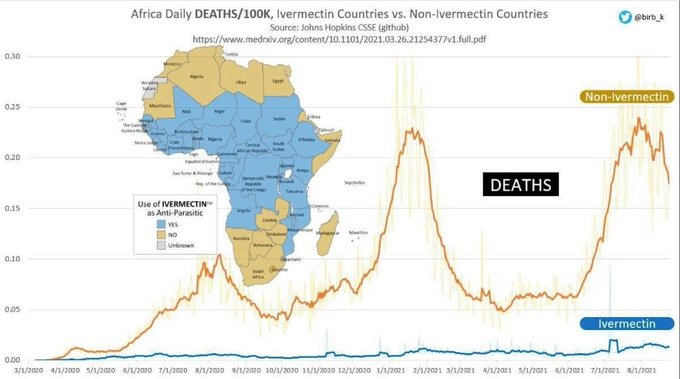
This image is the Ukraine 2012 election map and has been circulated to prove that Ukrainian citizens want to remain Russian-aligned. This argument has been endorsed by the Russian state media. The blue regions voted for a Russia-aligned political party, while the pink regions voted for a western aligned political party.
More recent 2019 parliamentary election maps provide a better understanding of Ukrainian interests. The party that Volodymyr Zelenskyy helped create, “Servant of the People” are portrayed in green. Parties in blue account for pro-Russian political parties, the “Opposition Platform,” and “Opposition Bloc.” These pro-Russian parties account for less than 17% of the parliamentary election votes. Ukraine’s parliamentary elections are similar to Germany’s, where half of the seats are determined by a “first past the post” system while the other half is determined by the popular majority. This system allows voters to support their favorite parties even if they are not competitive in the district they live in.
Ukraine does several rounds of presidential elections that filter out unpopular candidates each round. In 2019, Ukraine had 2 rounds of elections. The regions in blue are the only Pro-Russian candidates. These candidates were removed after the first round due to poor electoral performance. The second round of elections featured two pro-western candidates, Zelenskyy and Poroshenko. As you can see, the most recent elections prove that the overwhelming majority of Ukrainians do not want to be part of Russia.
Finding reliable information can be difficult. It is time-consuming and it can be difficult to navigate the current media landscape. Oftentimes we consume news passively, through social media and random headlines. Biasly can help with this through both its browser application, and its side-by-side news feature on its website.